本帖最后由 云天 于 2024-11-29 09:18 编辑 【项目背景】
在这个快节奏、高度数字化的时代,人们越来越渴望与智能设备进行更自然、更深入的交流。为了满足这一需求,我们推出了“轻松熊对话伴侣”——一个集成了最新人工智能技术的互动装置,旨在为用户提供一个既有趣又实用的对话伙伴。
【项目设计】
“轻松熊对话伴侣”项目的核心是一个搭载了ESP32-S3芯片的智能装置,它通过Micropython编程语言与Thonny软件的结合,实现了对MEMS麦克风阵列的精准控制和声音采集。用户只需简单按下按钮,装置便能捕捉到周围的声音,并利用urequests库将音频数据安全地发送至百度智能云进行语音识别。
识别后的文本信息将被进一步发送至百度千帆ModelBuilder大模型,这个强大的对话模型能够理解用户的意图并生成合适的回复。随后,这些文本回复将被转换成流畅自然的语音,通过百度语音合成技术实现。最后,ESP32-S3利用其I2S接口与MAX98357 I2S功放模块相连,将合成的音频信号传输至喇叭,播放出清晰、悦耳的声音。
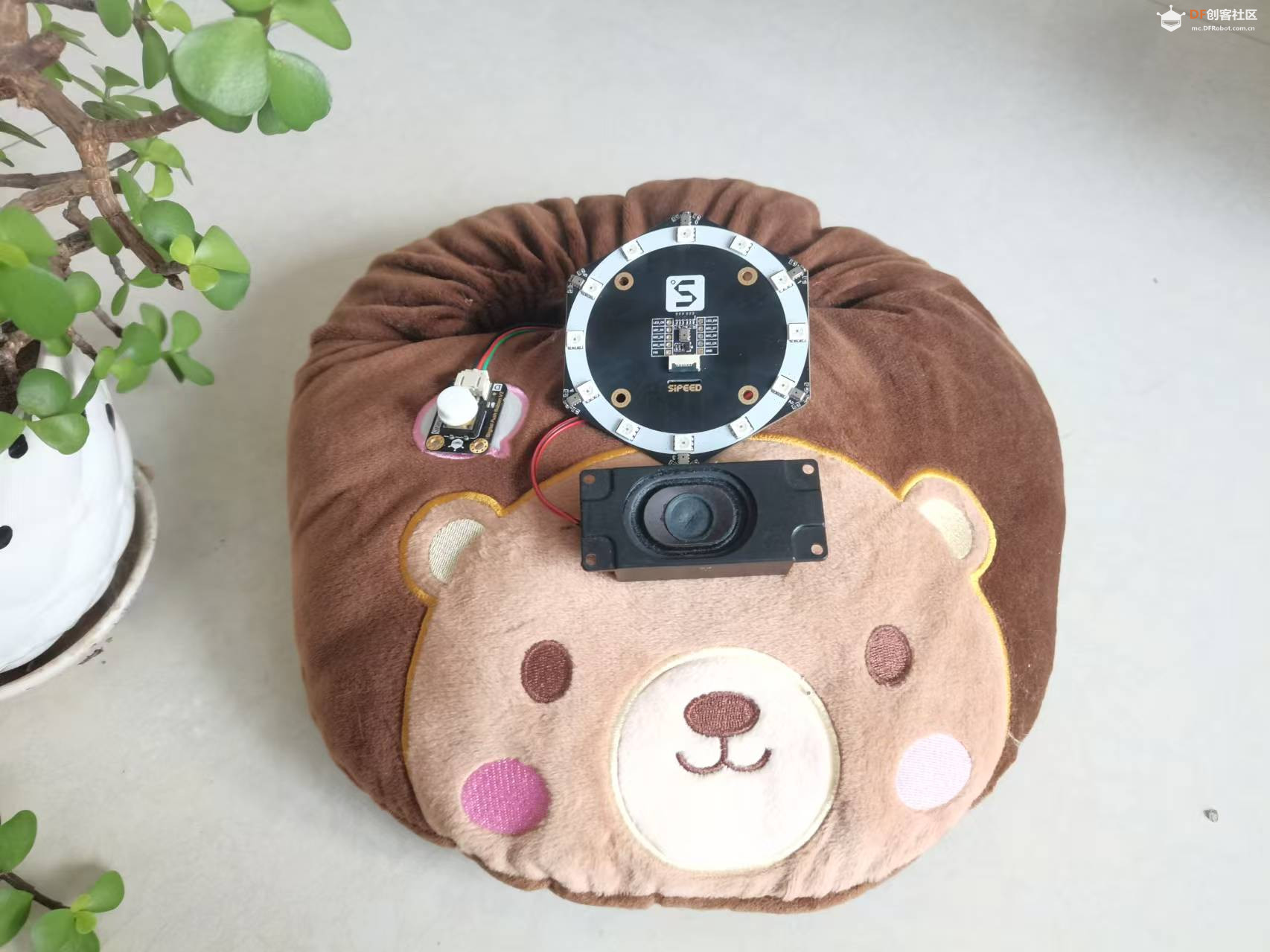
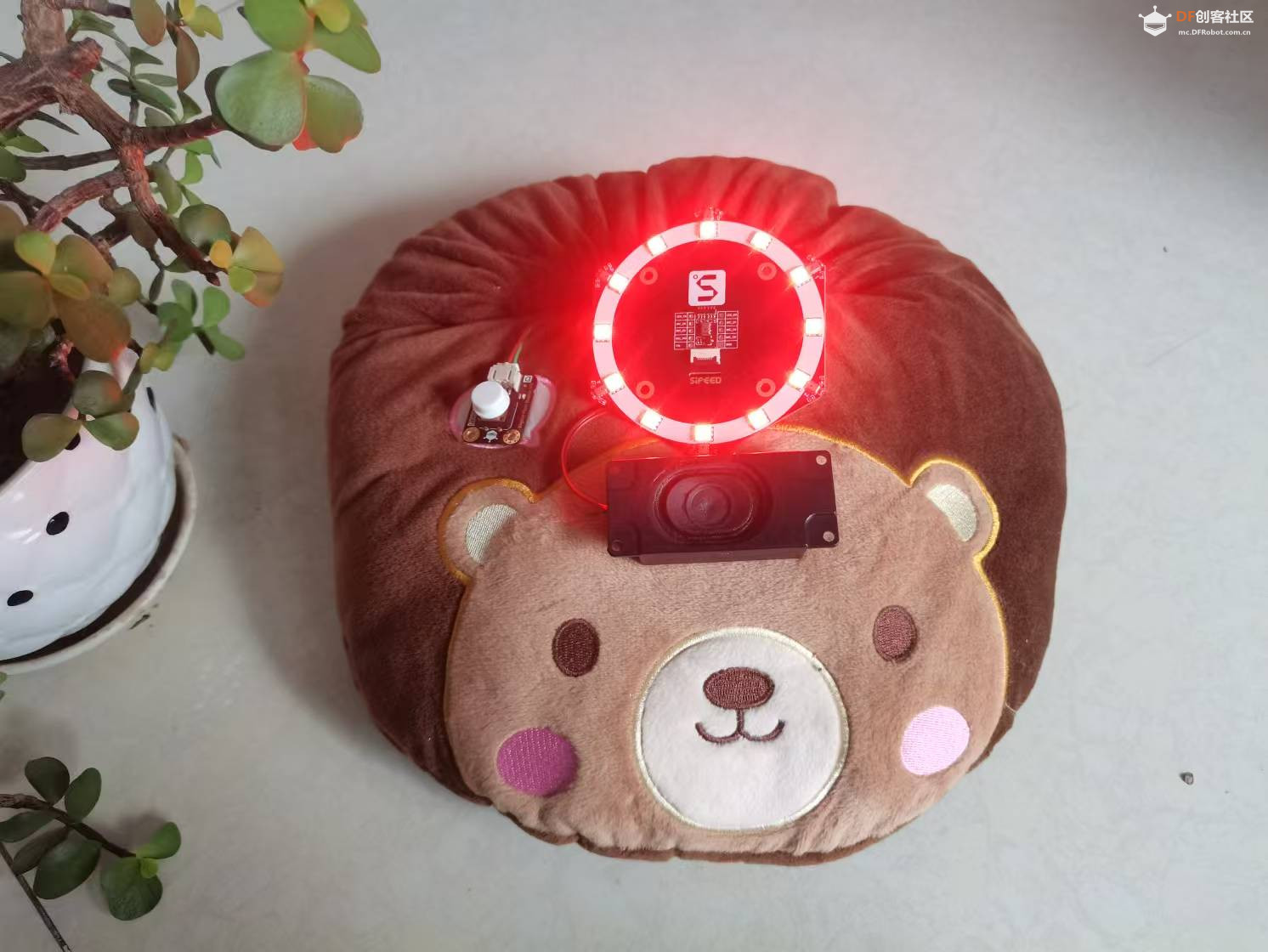
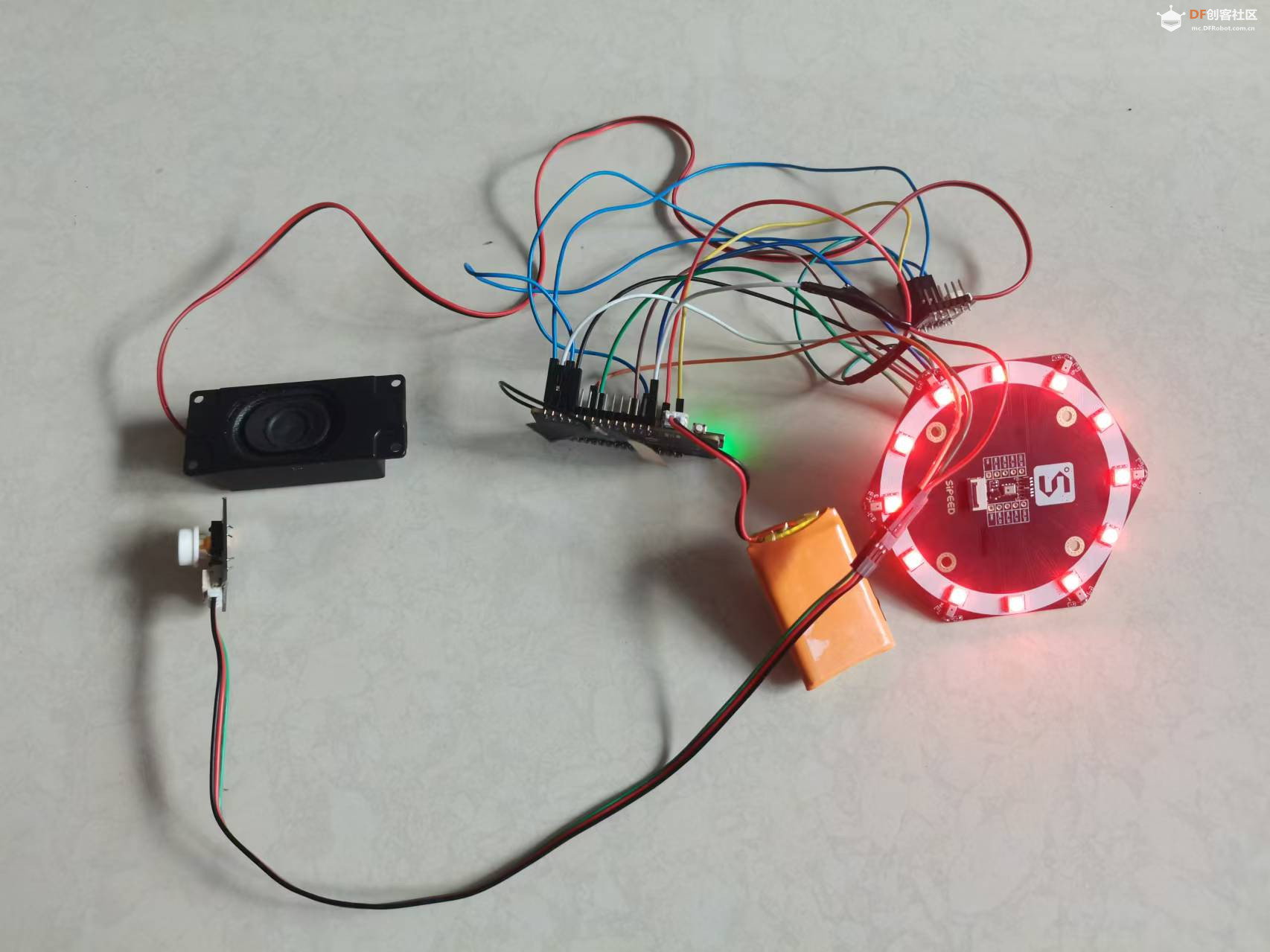
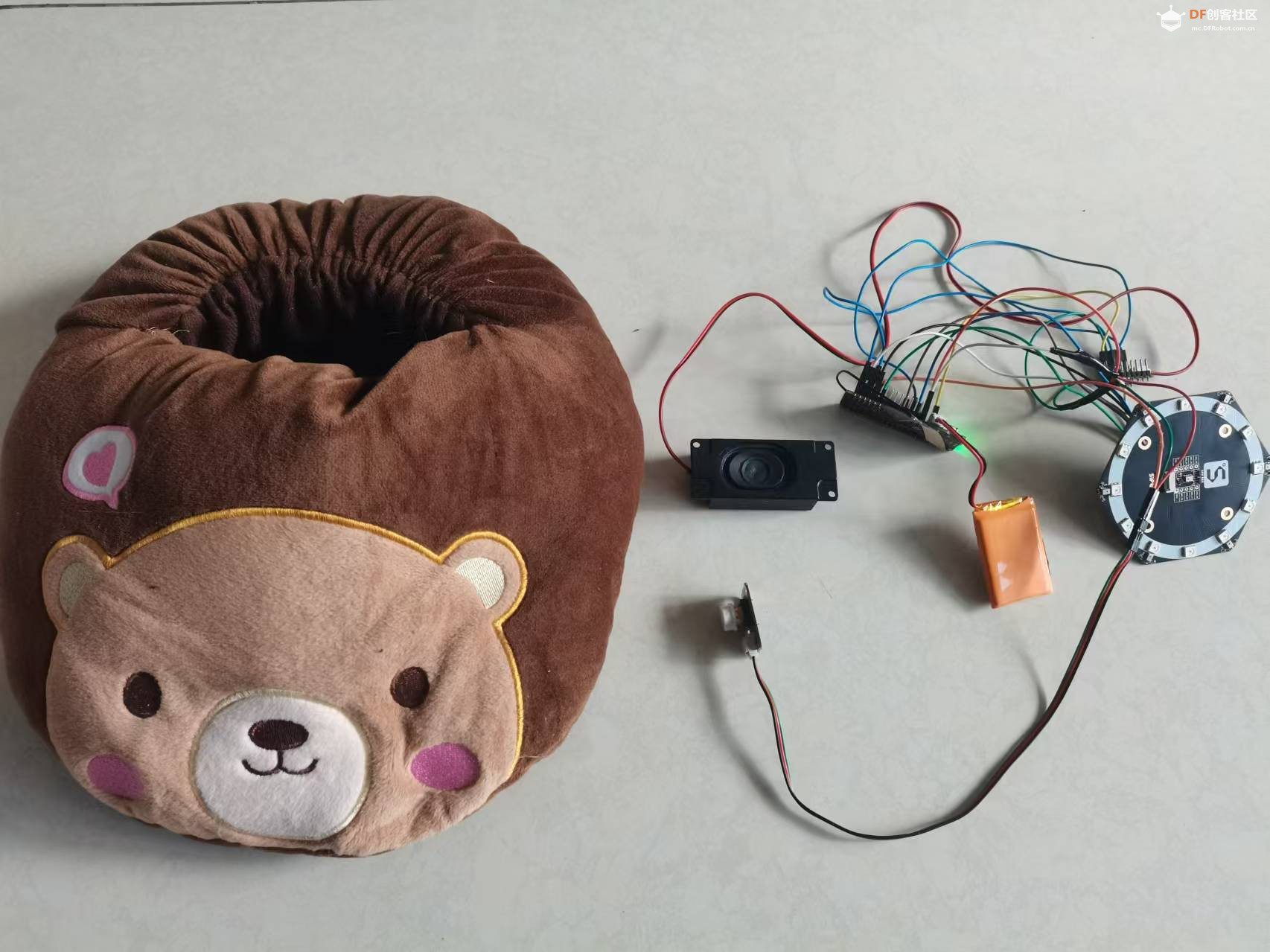
整个装置被巧妙地隐藏在一个可爱的轻松熊玩偶中,不仅增加了互动的趣味性,也使得技术与日常生活的融合更加自然和谐。无论是家庭娱乐、教育辅助还是简单的日常对话,“轻松熊对话伴侣”都能为用户提供一个温馨、智能的交流体验。
【项目硬件】 FireBeetle 2 ESP32-S3是一款基于ESP32-S3-WROOM-1-N16R8模组设计的主控板。ESP32-S3-WROOM-1-N16R8模组拥有16MB Flash和8MB PSRAM,可以存储更多的代码和数据,模组搭载的ESP32-S3芯片拥有强大的神经网络运算能力和信号处理能力,适用于图像识别、语音识别等项目。 【硬件电路】 1.# 定义功放I2S引脚 2.定义MEMS的麦克风I2S引脚 3.定义按钮引脚 【获取百度access_token】 【编写程序】
1.程序初始化
import machine
import time
import struct
from machine import Pin, I2S,SoftSPI
import micropython_dotstar as dotstar
import network
import urequests
import ujson
import ubinascii
import gc
# 定义I2S引脚
blck_pin = Pin(14)
lrc_pin = Pin(12)
din_pin = Pin(15)
# 初始化功放I2S
audio_out = I2S(
1,
sck=blck_pin, ws=lrc_pin, sd=din_pin,
mode=I2S.TX,
bits=16,
format=machine.I2S.MONO,
rate=16000,
ibuf=4096
)
# 定义麦克风I2S配置
i2s = machine.I2S(
0,
sck=machine.Pin(17),
ws=machine.Pin(18),
sd=machine.Pin(16),
mode=machine.I2S.RX,
bits=16,
format=machine.I2S.MONO,
rate=16000,
ibuf=4096
)
#定义麦克风上LED
spi = SoftSPI(sck=Pin(13), mosi=Pin(21), miso=Pin(3))
dots = dotstar.DotStar(spi, 12, brightness=0.2)
复制代码 2.连接WIFI函数
def connect_to_wifi(ssid, password):
wlan = network.WLAN(network.STA_IF) # 创建WLAN对象
wlan.active(True) # 激活接口
if not wlan.isconnected(): # 如果尚未连接到WiFi
print('正在连接到网络...')
wlan.connect(ssid, password) # 连接到指定的WiFi网络
while not wlan.isconnected(): # 等待直到连接成功
pass
print('网络配置:', wlan.ifconfig()) # 打印网络配置信息
def connect_wifi():
# 替换为你的WiFi SSID和密码
#ssid = "TP-LINK_CB88"
#password = "jiaoyan2"
ssid = "sxs"
password = "smj080823"
connect_to_wifi(ssid, password)
复制代码 3.播放音频函数
def play_audio(filename):
with open(filename, 'rb') as f:
f.seek(44) # 跳过头部信息
# 播放音频数据
while True:
data = f.read(1024) # 每次读取1024字节的数据
if not data:
break
audio_out.write(data)
复制代码 4.录制音频函数
def write_wav_header(file, sample_rate, bits_per_sample, channels):
num_channels = channels
bytes_per_sample = bits_per_sample // 8
byte_rate = sample_rate * num_channels * bytes_per_sample
block_align = num_channels * bytes_per_sample
# Write the WAV file header
file.write(b'RIFF')
file.write(struct.pack('<I', 36)) # Chunk size (36 + SubChunk2Size)
file.write(b'WAVE')
file.write(b'fmt ')
file.write(struct.pack('<I', 16)) # Subchunk1Size (PCM header size)
file.write(struct.pack('<H', 1)) # AudioFormat (PCM)
file.write(struct.pack('<H', num_channels)) # NumChannels
file.write(struct.pack('<I', sample_rate)) # SampleRate
file.write(struct.pack('<I', byte_rate)) # ByteRate
file.write(struct.pack('<H', block_align)) # BlockAlign
file.write(struct.pack('<H', bits_per_sample)) # BitsPerSample
file.write(b'data')
file.write(struct.pack('<I', 0)) # Subchunk2Size (to be filled later)
def record(filename,re_time):
audio_buffer = bytearray(4096)
sample_rate = 16000
bits_per_sample = 16
channels = 1
duration = re_time # Record for 5 seconds
print("开始录音")
play_audio("start.wav")#播放音频
with open(filename, 'wb') as f:
write_wav_header(f, sample_rate, bits_per_sample, channels)
subchunk2_size = 0
start_time = time.ticks_ms()
end_time = start_time + duration * 1000
try:
while time.ticks_ms() < end_time and not(button_state()):
num_bytes = i2s.readinto(audio_buffer)
if num_bytes > 0:
f.write(audio_buffer[:num_bytes])
subchunk2_size += num_bytes
time.sleep(0.01)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("Recording stopped")
# Go back and update the Subchunk2Size in the WAV header
f.seek(40)
f.write(struct.pack('<I', subchunk2_size))
f.seek(4)
f.write(struct.pack('<I', 36 + subchunk2_size))
print("录音结束")
play_audio("end.wav")#播放音频
复制代码 5.URL 编码
def urlencode(params):#编码成 URL 编码格式的字符串
encoded_pairs = []
for key, value in params.items():
# 确保键和值都是字符串
key_str = str(key)
value_str = str(value)
# 手动实现简单的URL编码
encoded_key = key_str.replace(" ", "%20")
encoded_value = value_str.replace(" ", "%20")
encoded_pairs.append(f"{encoded_key}={encoded_value}")
return "&".join(encoded_pairs)
复制代码 6.语音合成函数
def post_tts(filename,text, token):
# 设置请求参数
params = {
'tok': token,
'tex': text, # 直接使用text,不需要quote_plus
'per': 5,#基础音库:度小宇=1,度小美=0,度逍遥(基础)=3,度丫丫=4,精品音库:度逍遥(精品)=5003,度小鹿=5118,度博文=106,度小童=110,度小萌=111,度米朵=103,度小娇=5
'spd': 5,#中语速
'pit': 5,#中语调
'vol': 9,#中音量
'aue': 6,#wav,3为mp3格式(默认); 4为pcm-16k;5为pcm-8k;6为wav(内容同pcm-16k);
'cuid': "ZZloekkfqvZFKhpVtFXGlAopgnHnHCgQ",#用户唯一标识
'lan': 'zh',
'ctp': 1 #客户端类型选择,web端填写固定值1
}
headers = {
'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded',
'Accept': '*/*'
}
# 将参数编码,然后放入body,生成Request对象
data = urlencode(params).encode('utf-8')
# 发送POST请求
response = urequests.post("http://tsn.baidu.com/text2audio", headers=headers,data=data)
# 检查响应状态码
if response.status_code == 200:
# 将返回的音频数据写入文件
print("开始生成合成音频")
gc.collect() # 写入前收集垃圾
with open(filename, "wb") as f:
f.write(response.content)
gc.collect() # 写入后收集垃圾
print("完成生成合成音频")
else:
print("Failed to retrieve the MP3 file")
def tts(audio_file,text):#语音合成
token = '24.65578d0ef206e7de3a028e59691b2f1c.2592000.1735099609.282335-*******'
post_tts(audio_file,text,token)
复制代码 7.大模型对话
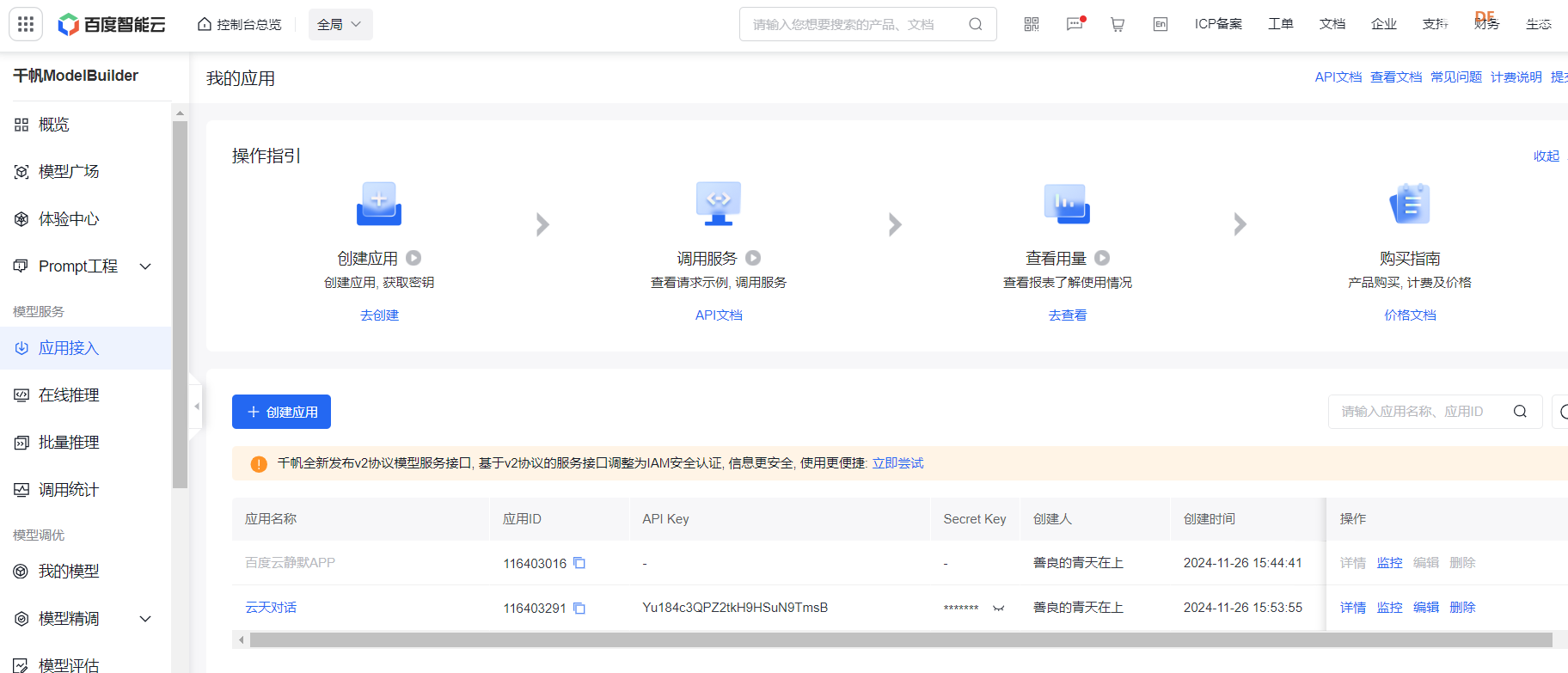
def spark(text):#大模型对话函数
#24.a56fc70c4012e7d9482f65b0eb896537.2592000.1735199722.282335-*******
API_KEY="Yu184c3QPZ2tkH9HSuN9TmsB"
SECRET_KEY="OcxUg0slEFB3nPrgchjQrBdsxfZUBM5q"
access_token="24.b4f3fc416c50a274a1f37a3f95083616.2592000.1735201337.282335-******"
#url = "https://aip.baidubce.com/rpc/2.0/ai_custom/v1/wenxinworkshop/chat/completions?access_token="+get_access_token(API_KEY,SECRET_KEY)
url = "https://aip.baidubce.com/rpc/2.0/ai_custom/v1/wenxinworkshop/chat/completions?access_token="+access_token
payload = {
"user_id": "yuntian365",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": text
}
],
"temperature": 0.95,
"top_p": 0.8,
"penalty_score": 1,
"enable_system_memory": False,
"disable_search": False,
"enable_citation": False,
"system": "请将回答控制在20字",
"response_format": "text"
}
header = {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
}
data_str = ujson.dumps(payload).encode('utf-8')
#print(data_str)
response = urequests.post(url,headers=header,data=data_str)
response_json=response.json()
#print(response_json)
response_content=response_json['result']
decoded_str = response_content.encode('utf-8').decode('unicode_escape')
print(decoded_str)
return(decoded_str)
复制代码 8.语音识别
def base64_encode(data):#base64编码
"""Base64 encode bytes-like objects"""
return ubinascii.b2a_base64(data)[:-1] # 去掉结果末尾的换行符
def get_access_token(API_KEY,SECRET_KEY):
url = "https://aip.baidubce.com/oauth/2.0/token"
params = {
'grant_type': 'client_credentials',
'client_id': API_KEY,
'client_secret': SECRET_KEY
}
data = urlencode(params).encode('utf-8')
response = urequests.post(url, data=data)
access_token=ujson.loads(response.text)['access_token']
print(access_token)
return access_token
def baidu_speech_recognize(audio_file, token):#百度语音识别
#url = "http://vop.baidu.com/server_api" #标准版
url = "https://vop.baidu.com/pro_api" #极速版
headers = {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'Accept': 'application/json'
}
with open(audio_file, "rb") as f:
audio_data = f.read()
base64_data = base64_encode(audio_data).decode('utf-8')
data = {
'format': 'wav',
'rate': 16000,
'channel': 1,
'token': token,
'cuid': "ESP32",
"dev_pid": 80001,#极速版,标准版去掉
'speech': base64_data,
'len': len(audio_data)
}
response = urequests.post(url, headers=headers, json=data)
return ujson.loads(response.text)
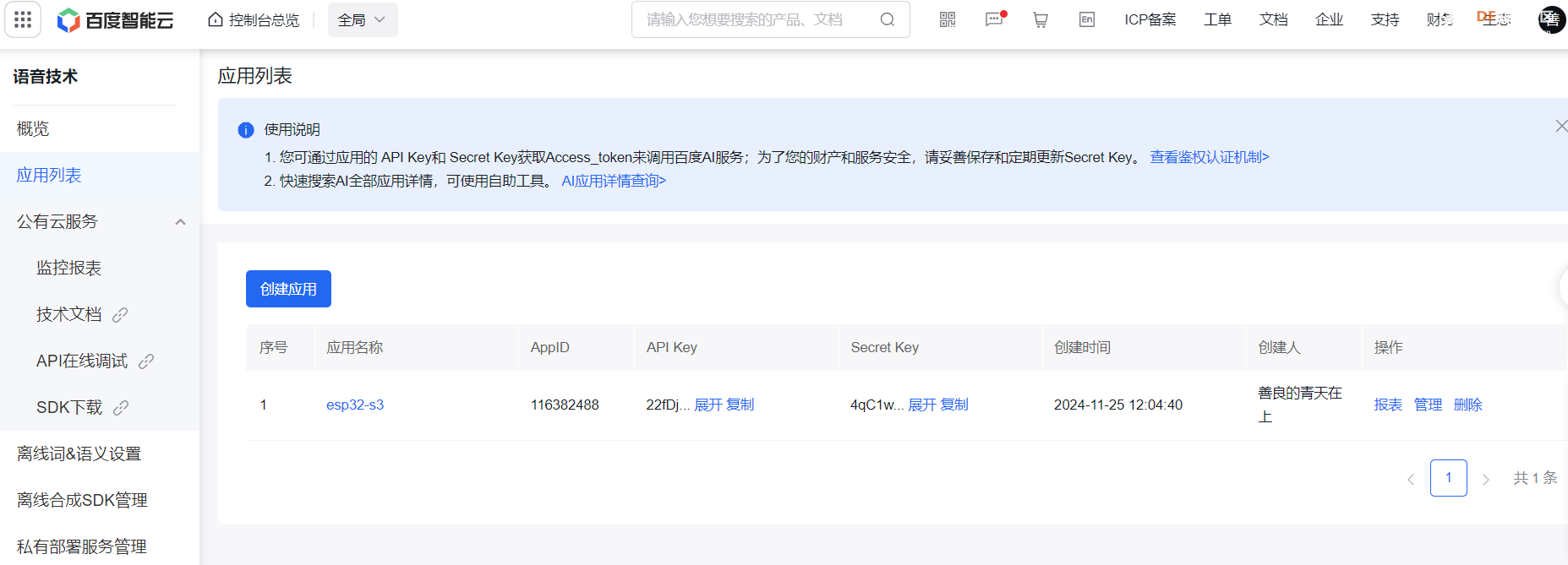
def speech(audio_file):#语音识别
# 替换为您的百度AI开放平台的API Key和Secret Key
API_KEY = "22fDjayW1nVOIP5tIAH8cODd"
SECRET_KEY = "4qC1wtOfKySgRM80NRId6rZ6CjVNrIWb"
# 获取access_token
#token = get_access_token(API_KEY,SECRET_KEY)
token = '24.65578d0ef206e7de3a028e59691b2f1c.2592000.1735099609.282335-116382488'
# 发送音频数据到百度语音识别API
result = baidu_speech_recognize(audio_file, token)
if result["err_no"]==0:
text=result["result"][0].encode('utf-8').decode('unicode_escape')
print(text)
return text
else:
return False
复制代码 9.麦克风上LED灯控制
def light_close():
n_dots = len(dots)
for dot in range(n_dots):
dots[dot] = (0, 0, 0)
def light_on():
n_dots = len(dots)
for dot in range(n_dots):
dots[dot] = (255, 0, 0)
复制代码 micropython_dotstar.py库文件:
# The MIT License (MIT)
#
# Copyright (c) 2016 Damien P. George (original Neopixel object)
# Copyright (c) 2017 Ladyada
# Copyright (c) 2017 Scott Shawcroft for Adafruit Industries
# Copyright (c) 2019 Matt Trentini (porting back to MicroPython)
#
# Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
# of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
# in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
# to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
# copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
# furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
#
# The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in
# all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
#
# THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
# IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
# FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
# AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
# LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
# OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN
# THE SOFTWARE.
"""
`micropython_dotstar` - DotStar strip driver
====================================================
* Author(s): Damien P. George, Limor Fried, Scott Shawcroft, Matt Trentini
"""
__version__ = "0.0.0-auto.0"
__repo__ = "https://github.com/mattytrentini/micropython-dotstar"
START_HEADER_SIZE = 4
LED_START = 0b11100000 # Three "1" bits, followed by 5 brightness bits
# Pixel color order constants
RGB = (0, 1, 2)
RBG = (0, 2, 1)
GRB = (1, 0, 2)
GBR = (1, 2, 0)
BRG = (2, 0, 1)
BGR = (2, 1, 0)
class DotStar:
"""
A sequence of dotstars.
:param SPI spi: The SPI object to write output to.
:param int n: The number of dotstars in the chain
:param float brightness: Brightness of the pixels between 0.0 and 1.0
:param bool auto_write: True if the dotstars should immediately change when
set. If False, `show` must be called explicitly.
:param tuple pixel_order: Set the pixel order on the strip - different
strips implement this differently. If you send red, and it looks blue
or green on the strip, modify this! It should be one of the values above
Example for TinyPICO:
.. code-block:: python
from micropython_dotstar import DotStar
from machine import Pin, SPI
spi = SPI(sck=Pin(12), mosi=Pin(13), miso=Pin(18)) # Configure SPI - note: miso is unused
dotstar = DotStar(spi, 1)
dotstar[0] = (128, 0, 0) # Red
"""
def __init__(self, spi, n, *, brightness=1.0, auto_write=True,
pixel_order=BGR):
self._spi = spi
self._n = n
# Supply one extra clock cycle for each two pixels in the strip.
self.end_header_size = n // 16
if n % 16 != 0:
self.end_header_size += 1
self._buf = bytearray(n * 4 + START_HEADER_SIZE + self.end_header_size)
self.end_header_index = len(self._buf) - self.end_header_size
self.pixel_order = pixel_order
# Four empty bytes to start.
for i in range(START_HEADER_SIZE):
self._buf[i] = 0x00
# Mark the beginnings of each pixel.
for i in range(START_HEADER_SIZE, self.end_header_index, 4):
self._buf[i] = 0xff
# 0xff bytes at the end.
for i in range(self.end_header_index, len(self._buf)):
self._buf[i] = 0xff
self._brightness = 1.0
# Set auto_write to False temporarily so brightness setter does _not_
# call show() while in __init__.
self.auto_write = False
self.brightness = brightness
self.auto_write = auto_write
def deinit(self):
"""Blank out the DotStars and release the resources."""
self.auto_write = False
for i in range(START_HEADER_SIZE, self.end_header_index):
if i % 4 != 0:
self._buf[i] = 0
self.show()
if self._spi:
self._spi.deinit()
def __enter__(self):
return self
def __exit__(self, exception_type, exception_value, traceback):
self.deinit()
def __repr__(self):
return "[" + ", ".join([str(x) for x in self]) + "]"
def _set_item(self, index, value):
"""
value can be one of three things:
a (r,g,b) list/tuple
a (r,g,b, brightness) list/tuple
a single, longer int that contains RGB values, like 0xFFFFFF
brightness, if specified should be a float 0-1
Set a pixel value. You can set per-pixel brightness here, if it's not passed it
will use the max value for pixel brightness value, which is a good default.
Important notes about the per-pixel brightness - it's accomplished by
PWMing the entire output of the LED, and that PWM is at a much
slower clock than the rest of the LEDs. This can cause problems in
Persistence of Vision Applications
"""
offset = index * 4 + START_HEADER_SIZE
rgb = value
if isinstance(value, int):
rgb = (value >> 16, (value >> 8) & 0xff, value & 0xff)
if len(rgb) == 4:
brightness = value[3]
# Ignore value[3] below.
else:
brightness = 1
# LED startframe is three "1" bits, followed by 5 brightness bits
# then 8 bits for each of R, G, and B. The order of those 3 are configurable and
# vary based on hardware
# same as math.ceil(brightness * 31) & 0b00011111
# Idea from https://www.codeproject.com/Tips/700780/Fast-floor-ceiling-functions
brightness_byte = 32 - int(32 - brightness * 31) & 0b00011111
self._buf[offset] = brightness_byte | LED_START
self._buf[offset + 1] = rgb[self.pixel_order[0]]
self._buf[offset + 2] = rgb[self.pixel_order[1]]
self._buf[offset + 3] = rgb[self.pixel_order[2]]
def __setitem__(self, index, val):
if isinstance(index, slice):
start, stop, step = index.indices(self._n)
length = stop - start
if step != 0:
# same as math.ceil(length / step)
# Idea from https://fizzbuzzer.com/implement-a-ceil-function/
length = (length + step - 1) // step
if len(val) != length:
raise ValueError("Slice and input sequence size do not match.")
for val_i, in_i in enumerate(range(start, stop, step)):
self._set_item(in_i, val[val_i])
else:
self._set_item(index, val)
if self.auto_write:
self.show()
def __getitem__(self, index):
if isinstance(index, slice):
out = []
for in_i in range(*index.indices(self._n)):
out.append(
tuple(self._buf[in_i * 4 + (3 - i) + START_HEADER_SIZE] for i in range(3)))
return out
if index < 0:
index += len(self)
if index >= self._n or index < 0:
raise IndexError
offset = index * 4
return tuple(self._buf[offset + (3 - i) + START_HEADER_SIZE]
for i in range(3))
def __len__(self):
return self._n
@property
def brightness(self):
"""Overall brightness of the pixel"""
return self._brightness
@brightness.setter
def brightness(self, brightness):
self._brightness = min(max(brightness, 0.0), 1.0)
if self.auto_write:
self.show()
def fill(self, color):
"""Colors all pixels the given ***color***."""
auto_write = self.auto_write
self.auto_write = False
for i in range(self._n):
self[i] = color
if auto_write:
self.show()
self.auto_write = auto_write
def show(self):
"""Shows the new colors on the pixels themselves if they haven't already
been autowritten.
The colors may or may not be showing after this function returns because
it may be done asynchronously."""
# Create a second output buffer if we need to compute brightness
buf = self._buf
if self.brightness < 1.0:
buf = bytearray(self._buf)
# Four empty bytes to start.
for i in range(START_HEADER_SIZE):
buf[i] = 0x00
for i in range(START_HEADER_SIZE, self.end_header_index):
buf[i] = self._buf[i] if i % 4 == 0 else int(self._buf[i] * self._brightness)
# Four 0xff bytes at the end.
for i in range(self.end_header_index, len(buf)):
buf[i] = 0xff
if self._spi:
self._spi.write(buf)
复制代码 10.按钮控制函数
BUTTON_PIN = 7
button = Pin(BUTTON_PIN, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_UP)
prev_button_state = 0
def button_state():
global button,prev_button_state
button_state = button.value()
if prev_button_state == 0 and button_state == 1:
print("The button is pressed")
if prev_button_state == 1 and button_state == 0:
print("The button is released")
prev_button_state = button_state
return True
prev_button_state = button_state
#print(prev_button_state)
return False
复制代码
if __name__ == "__main__":
light_close()
audio_file = "audio.wav"
connect_wifi()#连接Wifi
play_audio("init.wav")
while True:
if button_state():
light_on()
record(audio_file,10)#录音5秒
light_close()
result=speech(audio_file)#语音识别
if result!=False:
text=spark(result)#与大模型对话
tts(audio_file,text)#语音合成
play_audio(audio_file)#播放音频
else:
play_audio("again.wav")
复制代码 【完整程序】
import machine
import time
import struct
from machine import Pin, I2S,SoftSPI
import micropython_dotstar as dotstar
import network
import urequests
import ujson
import ubinascii
import gc
# 定义I2S引脚
blck_pin = Pin(14)
lrc_pin = Pin(12)
din_pin = Pin(15)
# 初始化I2S
audio_out = I2S(
1,
sck=blck_pin, ws=lrc_pin, sd=din_pin,
mode=I2S.TX,
bits=16,
format=machine.I2S.MONO,
rate=16000,
ibuf=4096
)
# I2S配置
i2s = machine.I2S(
0,
sck=machine.Pin(17),
ws=machine.Pin(18),
sd=machine.Pin(16),
mode=machine.I2S.RX,
bits=16,
format=machine.I2S.MONO,
rate=16000,
ibuf=4096
)
#定义麦克风上LED
spi = SoftSPI(sck=Pin(13), mosi=Pin(21), miso=Pin(3))
dots = dotstar.DotStar(spi, 12, brightness=0.2)
def connect_to_wifi(ssid, password):
wlan = network.WLAN(network.STA_IF) # 创建WLAN对象
wlan.active(True) # 激活接口
if not wlan.isconnected(): # 如果尚未连接到WiFi
print('正在连接到网络...')
wlan.connect(ssid, password) # 连接到指定的WiFi网络
while not wlan.isconnected(): # 等待直到连接成功
pass
print('网络配置:', wlan.ifconfig()) # 打印网络配置信息
def read_wav_header(filename):
with open(filename, 'rb') as f:
# Read the first 44 bytes (standard WAV header size)
header = f.read(44)
# Parse the header fields
chunk_id = header[0:4]
chunk_size = int.from_bytes(header[4:8], 'little')
format = header[8:12]
subchunk1_id = header[12:16]
subchunk1_size = int.from_bytes(header[16:20], 'little')
audio_format = int.from_bytes(header[20:22], 'little')
num_channels = int.from_bytes(header[22:24], 'little')
sample_rate = int.from_bytes(header[24:28], 'little')
byte_rate = int.from_bytes(header[28:32], 'little')
block_align = int.from_bytes(header[32:34], 'little')
bits_per_sample = int.from_bytes(header[34:36], 'little')
subchunk2_id = header[36:40]
subchunk2_size = int.from_bytes(header[40:44], 'little')
return {
'chunk_id': chunk_id,
'chunk_size': chunk_size,
'format': format,
'subchunk1_id': subchunk1_id,
'subchunk1_size': subchunk1_size,
'audio_format': audio_format,
'num_channels': num_channels,
'sample_rate': sample_rate,
'byte_rate': byte_rate,
'block_align': block_align,
'bits_per_sample': bits_per_sample,
'subchunk2_id': subchunk2_id,
'subchunk2_size': subchunk2_size
}
def write_wav_header(file, sample_rate, bits_per_sample, channels):
num_channels = channels
bytes_per_sample = bits_per_sample // 8
byte_rate = sample_rate * num_channels * bytes_per_sample
block_align = num_channels * bytes_per_sample
# Write the WAV file header
file.write(b'RIFF')
file.write(struct.pack('<I', 36)) # Chunk size (36 + SubChunk2Size)
file.write(b'WAVE')
file.write(b'fmt ')
file.write(struct.pack('<I', 16)) # Subchunk1Size (PCM header size)
file.write(struct.pack('<H', 1)) # AudioFormat (PCM)
file.write(struct.pack('<H', num_channels)) # NumChannels
file.write(struct.pack('<I', sample_rate)) # SampleRate
file.write(struct.pack('<I', byte_rate)) # ByteRate
file.write(struct.pack('<H', block_align)) # BlockAlign
file.write(struct.pack('<H', bits_per_sample)) # BitsPerSample
file.write(b'data')
file.write(struct.pack('<I', 0)) # Subchunk2Size (to be filled later)
def record(filename,re_time):
audio_buffer = bytearray(4096)
sample_rate = 16000
bits_per_sample = 16
channels = 1
duration = re_time # Record for 5 seconds
print("开始录音")
play_audio("start.wav")#播放音频
with open(filename, 'wb') as f:
write_wav_header(f, sample_rate, bits_per_sample, channels)
subchunk2_size = 0
start_time = time.ticks_ms()
end_time = start_time + duration * 1000
try:
while time.ticks_ms() < end_time and not(button_state()):
num_bytes = i2s.readinto(audio_buffer)
if num_bytes > 0:
f.write(audio_buffer[:num_bytes])
subchunk2_size += num_bytes
time.sleep(0.01)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("Recording stopped")
# Go back and update the Subchunk2Size in the WAV header
f.seek(40)
f.write(struct.pack('<I', subchunk2_size))
f.seek(4)
f.write(struct.pack('<I', 36 + subchunk2_size))
print("录音结束")
play_audio("end.wav")#播放音频
def play_audio(filename):
with open(filename, 'rb') as f:
f.seek(44) # 跳过头部信息
# 播放音频数据
while True:
data = f.read(1024) # 每次读取1024字节的数据
if not data:
break
audio_out.write(data)
def connect_wifi():
# 替换为你的WiFi SSID和密码
#ssid = "TP-LINK_CB88"
#password = "jiaoyan2"
ssid = "sxs"
password = "smj080823"
connect_to_wifi(ssid, password)
def urlencode(params):#编码成 URL 编码格式的字符串
encoded_pairs = []
for key, value in params.items():
# 确保键和值都是字符串
key_str = str(key)
value_str = str(value)
# 手动实现简单的URL编码
encoded_key = key_str.replace(" ", "%20")
encoded_value = value_str.replace(" ", "%20")
encoded_pairs.append(f"{encoded_key}={encoded_value}")
return "&".join(encoded_pairs)
def post_tts(filename,text, token):
# 设置请求参数
params = {
'tok': token,
'tex': text, # 直接使用text,不需要quote_plus
'per': 5,#基础音库:度小宇=1,度小美=0,度逍遥(基础)=3,度丫丫=4,精品音库:度逍遥(精品)=5003,度小鹿=5118,度博文=106,度小童=110,度小萌=111,度米朵=103,度小娇=5
'spd': 5,#中语速
'pit': 5,#中语调
'vol': 9,#中音量
'aue': 6,#wav,3为mp3格式(默认); 4为pcm-16k;5为pcm-8k;6为wav(内容同pcm-16k);
'cuid': "ZZloekkfqvZFKhpVtFXGlAopgnHnHCgQ",#用户唯一标识
'lan': 'zh',
'ctp': 1 #客户端类型选择,web端填写固定值1
}
headers = {
'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded',
'Accept': '*/*'
}
# 将参数编码,然后放入body,生成Request对象
data = urlencode(params).encode('utf-8')
# 发送POST请求
response = urequests.post("http://tsn.baidu.com/text2audio", headers=headers,data=data)
# 检查响应状态码
if response.status_code == 200:
# 将返回的音频数据写入文件
print("开始生成合成音频")
gc.collect() # 写入前收集垃圾
with open(filename, "wb") as f:
f.write(response.content)
gc.collect() # 写入后收集垃圾
print("完成生成合成音频")
else:
print("Failed to retrieve the MP3 file")
def tts(audio_file,text):#语音合成
token = '24.65578d0ef206e7de3a028e59691b2f1c.2592000.1735099609.282335-*******'
post_tts(audio_file,text,token)
def spark(text):#大模型对话函数
#24.a56fc70c4012e7d9482f65b0eb896537.2592000.1735199722.282335-******
API_KEY="Yu184c3QPZ2tkH9HSuN9TmsB"
SECRET_KEY="OcxUg0slEFB3nPrgchjQrBdsxfZUBM5q"
access_token="24.b4f3fc416c50a274a1f37a3f95083616.2592000.1735201337.282335-*******"
#url = "https://aip.baidubce.com/rpc/2.0/ai_custom/v1/wenxinworkshop/chat/completions?access_token="+get_access_token(API_KEY,SECRET_KEY)
url = "https://aip.baidubce.com/rpc/2.0/ai_custom/v1/wenxinworkshop/chat/completions?access_token="+access_token
payload = {
"user_id": "yuntian365",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": text
}
],
"temperature": 0.95,
"top_p": 0.8,
"penalty_score": 1,
"enable_system_memory": False,
"disable_search": False,
"enable_citation": False,
"system": "请将回答控制在20字",
"response_format": "text"
}
header = {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
}
data_str = ujson.dumps(payload).encode('utf-8')
#print(data_str)
response = urequests.post(url,headers=header,data=data_str)
response_json=response.json()
#print(response_json)
response_content=response_json['result']
decoded_str = response_content.encode('utf-8').decode('unicode_escape')
print(decoded_str)
return(decoded_str)
def base64_encode(data):#base64编码
"""Base64 encode bytes-like objects"""
return ubinascii.b2a_base64(data)[:-1] # 去掉结果末尾的换行符
def get_access_token(API_KEY,SECRET_KEY):
url = "https://aip.baidubce.com/oauth/2.0/token"
params = {
'grant_type': 'client_credentials',
'client_id': API_KEY,
'client_secret': SECRET_KEY
}
data = urlencode(params).encode('utf-8')
response = urequests.post(url, data=data)
access_token=ujson.loads(response.text)['access_token']
print(access_token)
return access_token
def baidu_speech_recognize(audio_file, token):#百度语音识别
#url = "http://vop.baidu.com/server_api" #标准版
url = "https://vop.baidu.com/pro_api" #极速版
headers = {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'Accept': 'application/json'
}
with open(audio_file, "rb") as f:
audio_data = f.read()
base64_data = base64_encode(audio_data).decode('utf-8')
data = {
'format': 'wav',
'rate': 16000,
'channel': 1,
'token': token,
'cuid': "ESP32",
"dev_pid": 80001,#极速版,标准版去掉
'speech': base64_data,
'len': len(audio_data)
}
response = urequests.post(url, headers=headers, json=data)
return ujson.loads(response.text)
def speech(audio_file):#语音识别
# 替换为您的百度AI开放平台的API Key和Secret Key
API_KEY = "22fDjayW1nVOIP5tIA******"
SECRET_KEY = "4qC1wtOfKySgRM80NRId6rZ6C******"
# 获取access_token
#token = get_access_token(API_KEY,SECRET_KEY)
token = '24.65578d0ef206e7de3a028e59691b2f1c.2592000.1735099609.282335-*********'
# 发送音频数据到百度语音识别API
result = baidu_speech_recognize(audio_file, token)
if result["err_no"]==0:
text=result["result"][0].encode('utf-8').decode('unicode_escape')
print(text)
return text
else:
return False
def light_close():
n_dots = len(dots)
for dot in range(n_dots):
dots[dot] = (0, 0, 0)
def light_on():
n_dots = len(dots)
for dot in range(n_dots):
dots[dot] = (255, 0, 0)
BUTTON_PIN = 7
button = Pin(BUTTON_PIN, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_UP)
prev_button_state = 0
def button_state():
global button,prev_button_state
button_state = button.value()
if prev_button_state == 0 and button_state == 1:
print("The button is pressed")
if prev_button_state == 1 and button_state == 0:
print("The button is released")
prev_button_state = button_state
return True
prev_button_state = button_state
#print(prev_button_state)
return False
if __name__ == "__main__":
light_close()
audio_file = "audio.wav"
connect_wifi()#连接Wifi
play_audio("init.wav")
while True:
if button_state():
light_on()
record(audio_file,10)#录音5秒
light_close()
result=speech(audio_file)#语音识别
if result!=False:
text=spark(result)#与大模型对话
tts(audio_file,text)#语音合成
play_audio(audio_file)#播放音频
else:
play_audio("again.wav")
复制代码 【thonny编程软件】 https://micropython.org/download/ 【演示视频】



 沪公网安备31011502402448
沪公网安备31011502402448